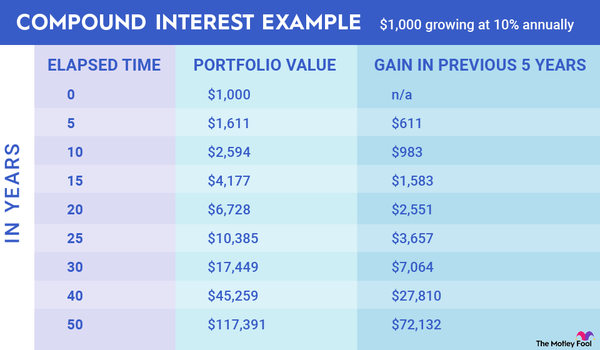
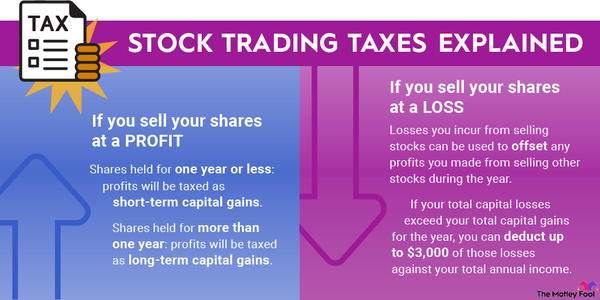
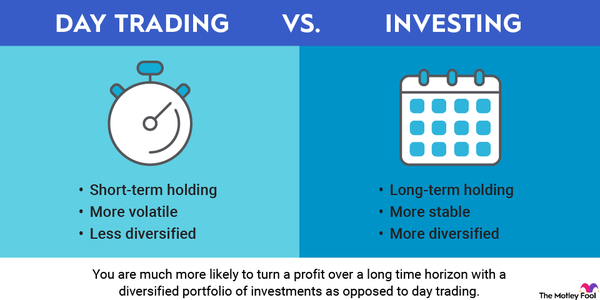
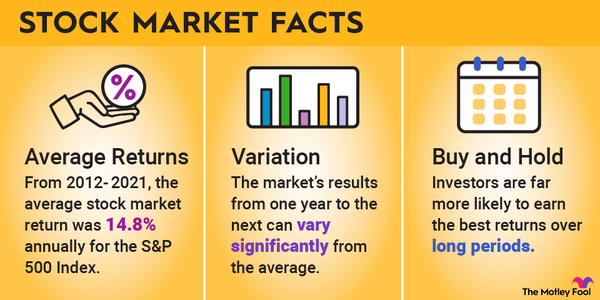
In the age of artificial intelligence (AI), Nvidia (NVDA -7.03%) has come to be the defining stock of the era. And not just because of the companies it owns.
The chipmaker, best known for its AI components based on graphics processing units (GPUs), has seen skyrocketing demand for its products since the launch of ChatGPT. Demand has soared because its chips are well suited to meeting the intense computing demands necessary to run generative AI models.
Much of Nvidia's growth has come organically. However, acquisitions have also played a role in its expanding semiconductor empire. No single acquisition has defined the company's growth -- that could have been Arm Holdings (ARM -2.58%), but regulators blocked the $40 billion deal. However, it has absorbed a number of smaller companies throughout its history.
More recently, it made headlines for taking minority stakes in several promising AI companies. Below, we'll take a look at how Nvidia stock has grown through acquisitions and how those deals fit into its current business.
What it owns
What companies does Nvidia own?
Nvidia's subsidiaries aren't exactly household names, but they have played a significant role in its evolution, running the gamut from AI companies to chip designers. Keep reading to see which companies are on the list.
1. Run:ai, 2024, 100% ownership
At the end of 2024, Nvidia closed on its $700 million acquisition of Run:ai. The company operates a platform on Kubernetes, which serves as the orchestration layer for modern AI and cloud infrastructure.
Run:ai has worked closely with Nvidia since 2020 and serves many of the world's biggest customers. The company will allow Nvidia's customers to access GPU solutions anywhere through a single fabric, improving utilization, infrastructure management, and flexibility.
Infrastructure
The deal took several months to pass regulatory muster, a sign that at a valuation of more than $3 trillion, Nvidia will have difficulty making acquisitions.
2. VinBrain, 2024, 100% ownership
In December 2024, Nvidia acquired VinBrain, a start-up that makes medical products that use AI. As part of the acquisition, Nvidia agreed to open two AI research and data centers in Vietnam, where VinBrain is based. The details of the acquisition were undisclosed. VinBrain was a division of Vingroup, which invested almost $5 million in the start-up in December 2023, so the buyout price was likely small.
3. OctoAI, 2024, 100% ownership
Another AI-focused acquisition Nvidia made in 2024 was OctoAI, a specialist in generative AI tools. Nvidia paid $250 million for OctoAI, formerly known as OctoML.
OctoAI is known for a technology that helps make AI hardware more accessible to developers with a hardware-agnostic software layer. It also supports popular large language models like Stable Diffusion and Meta's (META -3.54%) Llama.
4. Brev.dev, 2024, 100% ownership
In July 2024, Nvidia acquired Brev.dev, which helps AI developers find the lowest-priced GPU computers available from different cloud providers. The move seems designed to complement its fully managed AI platform, DGX Cloud service. Terms of the deal were undisclosed.
5. Shoreline, 2024, 100% ownership
Nvidia acquired Shoreline, an incident automation start-up, for a reported $100 million. Shoreline helps improve the reliability and efficiency of cloud-based services, providing a platform for companies to integrate observability tools and execute runbooks that allow customers to automate the identification of bugs and accelerate fixes.
6. Deci, 2024, 100% ownership
After Run:ai, Nvidia's biggest acquisition of 2024 appeared to be Deci, an Israeli AI start-up Nvidia acquired for a reported $300 million. Deci's focus is on automating deep-learning model design to improve performance. Nvidia has also established a research and development (R&D) center in Israel after making several acquisitions in the country.
7. OmniML, 2023, 100% ownership
Nvidia's biggest acquisition of 2023 was AI start-up OmniML. This included technology that helps miniaturize machine learning applications, such as large language models, so they can run on devices like computers, smartphones, and other end-user devices, known as edge devices. Nvidia didn't publicly announce the acquisition, a sign that it may not have wanted it to attract attention.
OmniML had just announced a partnership with Intel (INTC -2.9%) the month before Nvidia made its acquisition. It's unclear whether the deal will unwind the Intel partnership, but it seems likely, considering Intel and Nvidia are close competitors in AI.
Nvidia dominates the data center market in AI, but the edge market is a dogfight at the moment, with several chipmakers fighting for market share. The OmniML acquisition could give Nvidia an advantage. It's unclear how much Nvidia paid for OmniML.
8. Excelero Storage, 2022, 100% ownership
In March 2022, Nvidia acquired Excelero, an Israeli company founded in 2014 that specializes in providing high-performance storage solutions. It's known for its flagship product, NVMesh, which helps provide scalable and low-latency storage solutions.
Excelero has strengthened Nvidia's capabilities in AI and high-performance computing (HPC) and has been an Nvidia partner since its early days. Given this relationship, the acquisition made sense for Nvidia.
9. Bright Computing, 2022, 100% ownership
Bright Computing is yet another leader in HPC systems to fall under Nvidia's umbrella. Nvidia sees it playing an important role in areas like accelerated computing, GPUs, networking, its CUDA parallel computing platform, which simplifies the use of GPUs for general-purpose computing, and its DGX systems, which are Nvidia's line of servers to accelerate deep-learning applications.
Acquisitions like Bright Computing show that Nvidia's suite of AI-focused products is the result of a smart mergers and acquisitions strategy and its own product development.
10. Swiftstack, 2020, 100% ownership
In 2020, Nvidia made another acquisition to help build its supercomputer strategy: SwiftStack. This software-defined storage platform helps organizations store large volumes of unstructured data.
Like some of Nvidia's other acquisition targets, SwiftStack was expected to help with AI, HPC, and accelerated computing. It was unclear how much Nvidia paid for SwiftStack, although it had raised $23.6 million in its first two funding rounds and serves customers like PayPal (PYPL -2.68%), Verizon (VZ -1.85%), and Nvidia.
11. Mellanox Technologies, 2019, 100% ownership
The biggest acquisition in Nvidia's history was its $6.9 billion purchase of Mellanox, a company known for its high-performance networking technology. At the time of the 2019 acquisition, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang argued that Mellanox would fill out the company's end-to-end technologies, from AI computing to networking.
Nvidia also said it would unite the leaders in processing and interconnecting in HPC, which played a key role in Nvidia's development of its AI technology and its emphasis on accelerated computing, which has paid off for the company and investors.
12. SoundHound AI, 2023, $1.7 million, 0.6% ownership
Nvidia revealed several investments in AI stocks in its 13-F filing in February 2024. One of the more intriguing was SoundHound AI (SOUN -5.77%), a maker of audio AI technology that can perform tasks that include speech recognition, text-to-speech, and song identification.
Nvidia made a small investment in SoundHound in the fourth quarter, buying $1.73 million worth of stock. However, the value of its investment has gone up considerably since then.
Since SoundHound is more of an application-based, consumer-facing AI company, it seems unlikely the two companies would work directly together. But Nvidia could expand into new markets where SoundHound's technology could apply.
13. Arm Holdings, 2023, 0.2% ownership
Nvidia tried to buy chipmaker Arm Holdings in 2020, but regulators blocked the deal. The two have been close partners since then. Nvidia licenses Arm's architecture for products like the Grace Hopper H200 Superchip.
Arm is known for making efficient central processing units (CPUs) that consume less power than competitors like the x86 from Intel or AMD (AMD -7.42%). That's why Arm's designs are in 99% of smartphones, and its architecture is prized for running AI applications in data centers, which are especially power-hungry.
Nvidia's $147.3 million bet on Arm has already paid off. The stock soared on its fourth-quarter earnings report, and it wouldn't be surprising to see Nvidia build its stake in Arm over time.
14. Recursion Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 3.4% ownership
Nvidia announced a $50 million investment in Recursion Pharmaceuticals (RXRX -5.67%) in July 2023. Recursion is a biotech firm known for using AI models for drug discovery.
The announcement led Recursion stock to jump 80% as investors interpreted the news as a clear stamp of approval for Recursion from the AI leader. The two companies will also partner to train Recursion's AI models on Nvidia's cloud platform, which can then be licensed on BioNeMo, the generative AI-based drug discovery engine Nvidia launched in 2023.
Nvidia has increasingly touted its potential in healthcare, especially in areas like drug discovery. So, it wouldn't be surprising to see the company make more moves like this one or strengthen its relationship with Recursion in the future.
15. Nano-X Imaging, 2023, 0.1% ownership
Nvidia also revealed a stake in Nano-X Imaging (NNOX -4.25%), which seeks to disrupt conventional X-rays with its digital imaging technology. However, Nvidia didn't buy shares in Nano-X directly. Instead, Nvidia acquired the stake because its venture fund bought shares of Zebra Medical in 2017, which Nano-X acquired in 2021 in an all-stock deal worth roughly $200 million.
Venture Capital
However, Nvidia's decision to hold on to those shares acts as a kind of endorsement for Nano-X, which has struggled since its initial pop after it became publicly traded. Nano-X's ownership of Zebra Medical gives it exposure to AI since the company uses AI algorithms to find undetected signs of chronic diseases.
At just $380,000, Nvidia's stake in Nano-X is tiny. However, if its technology does pay off, there's a lot of upside for Nvidia.
16. Serve Robotics, 2024, 8.4% ownership
Serve Robotics, which recently went public, is another company in which Nvidia has taken a small, arguably speculative stake. Serve Robotics makes autonomous food delivery robots that move along sidewalks.
It's signed up Uber (UBER -1.34%) Eats, Yum! Brands' (YUM -1.38%) Pizza Hut, and Shake Shack (SHAK -2.6%) as customers. However, Serve Robotics is still a development-stage company with less than $1 million annual run-rate revenue as of the third quarter of 2024.
17. Applied Digital, 2024, 3.6% ownership
Nvidia invested $160 million in Applied Digital (APLD 18.17%), a company that designs and operates data centers and cloud services to support customers with HPC needs. Applied Digital seems like a natural partner for Nvidia, so it's no surprise to see Nvidia accumulating a stake in the company.
Potential buys
What companies could Nvidia buy in the future?
Given its acquisition history and recent minority investments, there is a wide range of companies Nvidia could potentially acquire. The company clearly sees healthcare as a burgeoning field in AI, so it wouldn't be surprising to see it make more acquisitions in the health-tech field.
More acquisitions that would help the company strengthen its technology in accelerated computing also seem likely. Nvidia is launching PC chips for the first time, extending its leadership position in AI into PCs. Making an acquisition that would help that initiative also makes sense. Nvidia will again use Arm designs for the chipsets.
It's difficult to identify individual companies Nvidia could purchase, as the options range from start-ups to established publicly traded companies. But investors should expect Nvidia to continue strengthening and diversifying its positioning in AI through acquisitions.
Related investing topics
The bottom line on companies Nvidia owns
Nvidia owns a wide array of subsidiaries dating back to the company's early history. Those have played a key role in making the company one of the most valuable in the world.
These days, Nvidia is squarely focused on artificial intelligence. Almost all its recent acquisitions have been key to burnishing its AI credentials, whether by improving AI technology or entering new markets. Given the company's market-leading position in AI hardware, we will likely see more acquisitions from Nvidia in the coming years.
FAQ
Companies Nvidia owns: FAQ
What companies did Nvidia buy?
Nvidia has made several acquisitions in its history, the biggest of which was its $6.9 billion purchase of Mellanox in 2019. Mellanox supplies key networking technology, such as end-to-end high-speed Ethernet and InfiniBand interconnect solutions.
Nvidia tried to acquire chip design company Arm for $40 billion in 2020, but regulators blocked the deal. Instead, Nvidia bought a minority stake in Arm once it went public. Among the other companies Nvidia owns are Run:ai, OmniML, SwfitStack, Bright Computing, and Excelero Storage.
What is Nvidia's main product?
Nvidia is best known for its graphics processing unit (GPU), which underpins top-selling products like the H100 Superchip. Nvidia invented the GPU in 1999, which initially drove the growth of the PC gaming industry.
These days, Nvidia GPUs are highly valued for running AI applications like ChatGPT and other large language models, which have enormous computing demands. Nvidia has an estimated 98% share of the data center GPU market, giving it a virtual monopoly in a rapidly growing business.
Who owns Nvidia?
Nvidia has been public since 1999, and many of its biggest shareholders are insiders, like CEO Jensen Huang. As of March 25, 2024, Huang owned 93.5 million shares of the stock, or 3.8% of the company, worth roughly $130 billion today.
Some of its biggest institutional shareholders include the Vanguard Group, which owns 204.5 million shares, or 8.3% of the company; BlackRock (NYSE: BLK), which owns 180.6 million, a 7.3% stake in Nvidia; and FMR, which owns 127.9 million shares, giving it a 5.2% ownership stake of Nvidia.
How much of the market does Nvidia own?
The semiconductor market is vast and diversified, but Nvidia dominates the market of GPUs. It has an estimated 80% share of the global GPU semiconductor market and an estimated 98% share of data center GPUs, which are used to run high-powered AI models.